Greenland is the world's largest island, located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans. It is an autonomous territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, and its geographical location has made it an important part of world maps. In this article, we will discuss the significance of Greenland in world maps and its impact on global affairs.
Greenland's Location
Greenland is located in the Northern Hemisphere, between North America and Europe. It is part of the North American continent but is politically and culturally linked to Europe. Its location has made it a strategic point for military and economic purposes. Greenland's proximity to the Arctic region has also made it an important player in the global climate change debate.
Greenland's Size
Greenland is the world's largest island, covering an area of 2,166,086 square kilometers. Its size is significant because it affects global maps and projections. Greenland's size is often exaggerated on world maps, which can distort perceptions of its actual size.
Greenland's Resources
Greenland is rich in natural resources, including minerals, oil, and gas. Its resources have made it a target for international investment and exploration. However, the exploitation of these resources has also raised concerns about the impact on the environment and indigenous communities.
Greenland's People
Greenland has a population of approximately 56,000 people, mostly of Inuit and Danish descent. Its population density is one of the lowest in the world, with most people living in coastal towns and cities. Greenland's people and culture have a unique place in world maps, as they represent a distinct indigenous community.
Greenland's Sovereignty
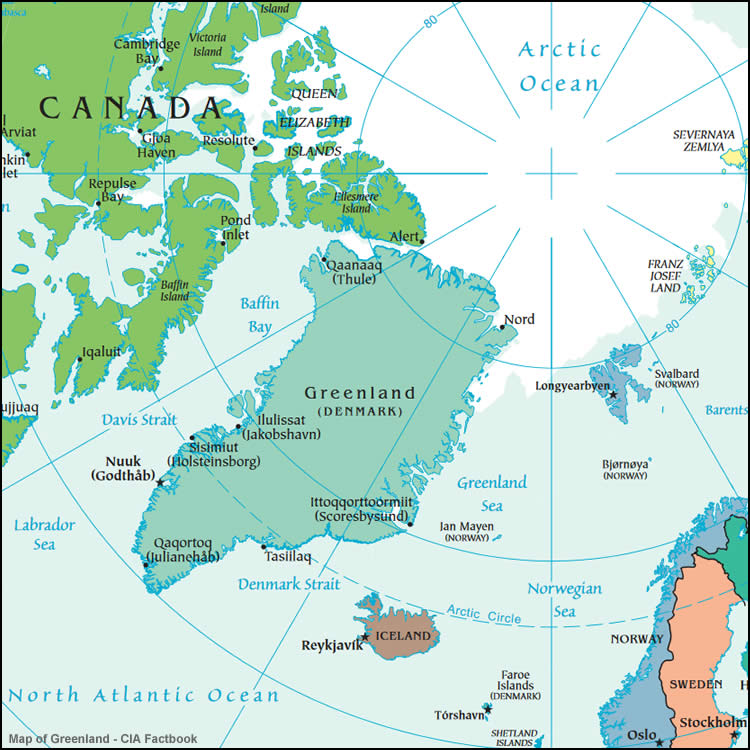
Greenland is an autonomous territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, but it has its own government and parliament. Its sovereignty has been a topic of debate, with some advocating for full independence from Denmark. Greenland's status as a semi-autonomous territory affects its representation on world maps and its role in global affairs.
Greenland's Climate
Greenland's climate is cold and polar, with long winters and short summers. Its climate has a significant impact on global weather patterns and sea levels. The melting of Greenland's ice sheet contributes to rising sea levels, which has implications for coastal cities and communities around the world.
Greenland's Tourism
Greenland's unique landscape and culture have made it a popular destination for tourists. Its tourism industry is focused on adventure and nature tourism, with activities such as dog sledding, hiking, and whale watching. Greenland's tourism industry affects global perceptions of the island and its people.
Greenland's Role in Global Affairs
Greenland's position as a strategic location, rich in natural resources, and with a unique culture and climate, has made it an important player in global affairs. Its sovereignty and relationship with Denmark have implications for the Arctic region and international politics. Greenland's role in global affairs affects its representation on world maps and its impact on the world stage.
Conclusion
Greenland's significance in world maps cannot be underestimated. Its location, size, resources, people, sovereignty, climate, tourism, and role in global affairs all contribute to its unique place in the world. As the world changes, Greenland's place in world maps and global affairs will continue to evolve.