The Himalayan Mountains are the highest and the youngest range in the world. They are located in Asia, covering a distance of about 2,400 km, and passing through countries like India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, and Pakistan. The Himalayas are known for their stunning beauty and extreme weather conditions, but they also play an important role in the tectonic activity of the Earth.
Formation of the Himalayan Mountains
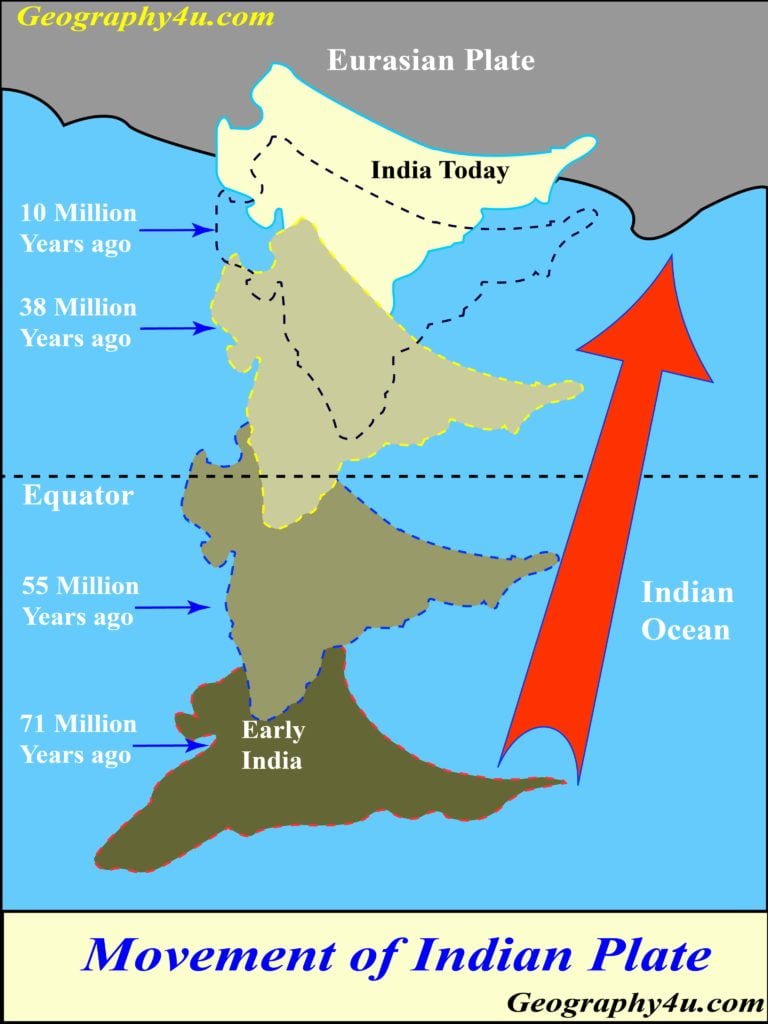
The Himalayas were formed due to the collision of the Indian and the Eurasian tectonic plates. The Indian plate was moving northwards towards the Eurasian plate at a speed of about 5 cm per year. About 50 million years ago, the Indian plate collided with the Eurasian plate, resulting in the formation of the Himalayan Mountains.
The collision of the two plates caused the Indian plate to move beneath the Eurasian plate, a process known as subduction. The subduction of the Indian plate caused the overlying Eurasian plate to buckle and fold, resulting in the formation of the Himalayan Mountains.
Geological Features of the Himalayas

The Himalayan Mountains are characterized by their high peaks, deep valleys, and steep slopes. They are home to some of the highest peaks in the world, including Mount Everest, the highest peak in the world. The Himalayas are also home to numerous glaciers, lakes, and rivers, which are an important source of water for the surrounding regions.
The Himalayas are divided into three main ranges: the Greater Himalayas, the Lesser Himalayas, and the Outer Himalayas. The Greater Himalayas are the highest range, with peaks reaching heights of over 8,000 meters. The Lesser Himalayas are lower in height, with peaks ranging between 3,700 and 4,500 meters. The Outer Himalayas are the lowest range, with peaks ranging between 900 and 1,500 meters.
Plate Boundary and Earthquakes

The Himalayan Mountains are located at the boundary between two tectonic plates, which makes them prone to earthquakes. The collision of the Indian and the Eurasian plates continues to this day, causing the Himalayan Mountains to rise at a rate of about 5mm per year.
The movement of the plates causes stress to build up in the rocks, which can result in earthquakes. The Himalayan region is one of the most seismically active regions in the world, with earthquakes occurring frequently. Some of the biggest earthquakes in history have occurred in the Himalayan region, causing widespread damage and loss of life.
Impact on the Environment

The Himalayan Mountains are home to a unique and diverse ecosystem, with numerous plant and animal species found only in this region. The mountains are also an important source of water for the surrounding regions, with numerous rivers and streams originating in the Himalayas.
However, the Himalayan ecosystem is under threat due to human activities like deforestation, mining, and tourism. These activities are causing soil erosion, landslides, and loss of habitat for wildlife. Climate change is also having a significant impact on the Himalayan region, with rising temperatures causing the glaciers to melt and altering the ecosystem.
Conclusion
The Himalayan Mountains are a fascinating and beautiful region, but they also play an important role in the tectonic activity of the Earth. The collision of the Indian and the Eurasian plates has resulted in the formation of this majestic mountain range, but it has also made the region prone to earthquakes. The Himalayas are also home to a unique and diverse ecosystem, which is under threat due to human activities and climate change.